How to Determine if Something is Continues in a Dervative

The graph of a function, drawn in black, and a tangent line to that graph, drawn in red. The slope of the tangent line is equal to the derivative of the function at the marked point.
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances.
The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable.
Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the derivative is reinterpreted as a linear transformation whose graph is (after an appropriate translation) the best linear approximation to the graph of the original function. The Jacobian matrix is the matrix that represents this linear transformation with respect to the basis given by the choice of independent and dependent variables. It can be calculated in terms of the partial derivatives with respect to the independent variables. For a real-valued function of several variables, the Jacobian matrix reduces to the gradient vector.
The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation. The reverse process is called antidifferentiation. The fundamental theorem of calculus relates antidifferentiation with integration. Differentiation and integration constitute the two fundamental operations in single-variable calculus.[Note 1]
Definition
A function of a real variable f(x) is differentiable at a point a of its domain, if its domain contains an open interval I containing a, and the limit
exists. This means that, for every positive real number (even very small), there exists a positive real number such that, for every h such that and then is defined, and
where the vertical bars denote the absolute value (see (ε, δ)-definition of limit).
If the function f is differentiable at a, that is if the limit L exists, then this limit is called the derivative of f at a, and denoted (read as " f prime of a ") or (read as "the derivative of f with respect to x at a", " dy by dx at a", or " dy over dx at a"); see § Notation (details), below.
Continuity and differentiability
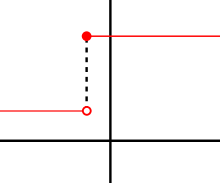
This function does not have a derivative at the marked point, as the function is not continuous there (specifically, it has a jump discontinuity).
If f is differentiable at a , then f must also be continuous at a . As an example, choose a point a and let f be the step function that returns the value 1 for all x less than a , and returns a different value 10 for all x greater than or equal to a . f cannot have a derivative at a . If h is negative, then a + h is on the low part of the step, so the secant line from a to a + h is very steep, and as h tends to zero the slope tends to infinity. If h is positive, then a + h is on the high part of the step, so the secant line from a to a + h has slope zero. Consequently, the secant lines do not approach any single slope, so the limit of the difference quotient does not exist.
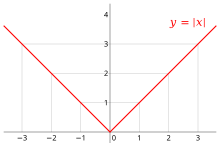
The absolute value function is continuous, but fails to be differentiable at x = 0 since the tangent slopes do not approach the same value from the left as they do from the right.
However, even if a function is continuous at a point, it may not be differentiable there. For example, the absolute value function given by f(x) = | x | is continuous at x = 0, but it is not differentiable there. If h is positive, then the slope of the secant line from 0 to h is one, whereas if h is negative, then the slope of the secant line from 0 to h is negative one. This can be seen graphically as a "kink" or a "cusp" in the graph at x = 0. Even a function with a smooth graph is not differentiable at a point where its tangent is vertical: For instance, the function given by f(x) = x 1/3 is not differentiable at x = 0.
In summary, a function that has a derivative is continuous, but there are continuous functions that do not have a derivative.
Most functions that occur in practice have derivatives at all points or at almost every point. Early in the history of calculus, many mathematicians assumed that a continuous function was differentiable at most points. Under mild conditions, for example if the function is a monotone function or a Lipschitz function, this is true. However, in 1872 Weierstrass found the first example of a function that is continuous everywhere but differentiable nowhere. This example is now known as the Weierstrass function. In 1931, Stefan Banach proved that the set of functions that have a derivative at some point is a meager set in the space of all continuous functions.[1] Informally, this means that hardly any random continuous functions have a derivative at even one point.
Derivative as a function
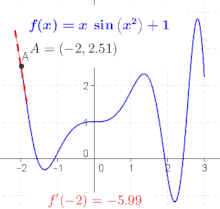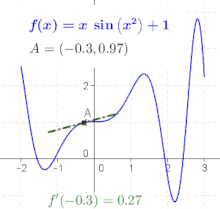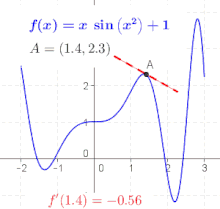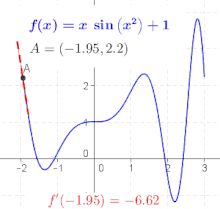
The derivative at different points of a differentiable function. In this case, the derivative is equal to:
Let f be a function that has a derivative at every point in its domain. We can then define a function that maps every point x to the value of the derivative of f at x. This function is written f ′ and is called the derivative function or the derivative of f .
Sometimes f has a derivative at most, but not all, points of its domain. The function whose value at a equals f ′(a) whenever f ′(a) is defined and elsewhere is undefined is also called the derivative of f . It is still a function, but its domain may be smaller than the domain of f .
Using this idea, differentiation becomes a function of functions: The derivative is an operator whose domain is the set of all functions that have derivatives at every point of their domain and whose range is a set of functions. If we denote this operator by D , then D(f) is the function f ′ . Since D(f) is a function, it can be evaluated at a point a. By the definition of the derivative function, D(f)(a) = f ′(a).
For comparison, consider the doubling function given by f(x) = 2x ; f is a real-valued function of a real number, meaning that it takes numbers as inputs and has numbers as outputs:
The operator D , however, is not defined on individual numbers. It is only defined on functions:
Because the output of D is a function, the output of D can be evaluated at a point. For instance, when D is applied to the square function, x ↦ x 2 , D outputs the doubling function x ↦ 2x , which we named f(x). This output function can then be evaluated to get f(1) = 2, f(2) = 4, and so on.
Higher derivatives
Let f be a differentiable function, and let f ′ be its derivative. The derivative of f ′ (if it has one) is written f ′′ and is called the second derivative of f . Similarly, the derivative of the second derivative, if it exists, is written f ′′′ and is called the third derivative of f . Continuing this process, one can define, if it exists, the n th derivative as the derivative of the (n−1)th derivative. These repeated derivatives are called higher-order derivatives. The n th derivative is also called the derivative of order n and denoted f (n) .
If x(t) represents the position of an object at time t , then the higher-order derivatives of x have specific interpretations in physics. The first derivative of x is the object's velocity. The second derivative of x is the acceleration. The third derivative of x is the jerk. And finally, the fourth through sixth derivatives of x are snap, crackle, and pop; most applicable to astrophysics.
A function f need not have a derivative (for example, if it is not continuous). Similarly, even if f does have a derivative, it may not have a second derivative. For example, let
Calculation shows that f is a differentiable function whose derivative at is given by
f'(x) is twice the absolute value function at , and it does not have a derivative at zero. Similar examples show that a function can have a k th derivative for each non-negative integer k but not a (k + 1)th derivative. A function that has k successive derivatives is called k times differentiable. If in addition the k th derivative is continuous, then the function is said to be of differentiability class Ck . (This is a stronger condition than having k derivatives, as shown by the second example of Smoothness § Examples.) A function that has infinitely many derivatives is called infinitely differentiable or smooth.
On the real line, every polynomial function is infinitely differentiable. By standard differentiation rules, if a polynomial of degree n is differentiated n times, then it becomes a constant function. All of its subsequent derivatives are identically zero. In particular, they exist, so polynomials are smooth functions.
The derivatives of a function f at a point x provide polynomial approximations to that function near x . For example, if f is twice differentiable, then
in the sense that
If f is infinitely differentiable, then this is the beginning of the Taylor series for f evaluated at x + h around x .
Inflection point
A point where the second derivative of a function changes sign is called an inflection point.[2] At an inflection point, the second derivative may be zero, as in the case of the inflection point x = 0 of the function given by , or it may fail to exist, as in the case of the inflection point x = 0 of the function given by . At an inflection point, a function switches from being a convex function to being a concave function or vice versa.
Notation (details)
Leibniz's notation
The symbols , , and were introduced by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in 1675.[3] It is still commonly used when the equation y = f(x) is viewed as a functional relationship between dependent and independent variables. Then the first derivative is denoted by
and was once thought of as an infinitesimal quotient. Higher derivatives are expressed using the notation
for the nth derivative of . These are abbreviations for multiple applications of the derivative operator. For example,
With Leibniz's notation, we can write the derivative of at the point in two different ways:
Leibniz's notation allows one to specify the variable for differentiation (in the denominator), which is relevant in partial differentiation. It also can be used to write the chain rule as[Note 2]
Lagrange's notation
Sometimes referred to as prime notation,[4] one of the most common modern notations for differentiation is due to Joseph-Louis Lagrange and uses the prime mark, so that the derivative of a function is denoted . Similarly, the second and third derivatives are denoted
- and
To denote the number of derivatives beyond this point, some authors use Roman numerals in superscript, whereas others place the number in parentheses:
- or
The latter notation generalizes to yield the notation for the nth derivative of – this notation is most useful when we wish to talk about the derivative as being a function itself, as in this case the Leibniz notation can become cumbersome.
Newton's notation
Newton's notation for differentiation, also called the dot notation, places a dot over the function name to represent a time derivative. If , then
- and
denote, respectively, the first and second derivatives of . This notation is used exclusively for derivatives with respect to time or arc length. It is typically used in differential equations in physics and differential geometry.[5] [6] The dot notation, however, becomes unmanageable for high-order derivatives (order 4 or more) and cannot deal with multiple independent variables.
Euler's notation
Euler's notation uses a differential operator , which is applied to a function to give the first derivative . The nth derivative is denoted .
If y = f(x) is a dependent variable, then often the subscript x is attached to the D to clarify the independent variable x. Euler's notation is then written
- or ,
although this subscript is often omitted when the variable x is understood, for instance when this is the only independent variable present in the expression.
Euler's notation is useful for stating and solving linear differential equations.
Rules of computation
The derivative of a function can, in principle, be computed from the definition by considering the difference quotient, and computing its limit. In practice, once the derivatives of a few simple functions are known, the derivatives of other functions are more easily computed using rules for obtaining derivatives of more complicated functions from simpler ones.
Rules for basic functions
Here are the rules for the derivatives of the most common basic functions, where a is a real number.
- Derivatives of powers:
- Exponential and logarithmic functions:
- Trigonometric functions:
- Inverse trigonometric functions:
Rules for combined functions
Here are some of the most basic rules for deducing the derivative of a compound function from derivatives of basic functions.
Computation example
The derivative of the function given by
is
Here the second term was computed using the chain rule and third using the product rule. The known derivatives of the elementary functions x 2, x 4, sin(x), ln(x) and exp(x) = e x , as well as the constant 7, were also used.
Definition with hyperreals
Relative to a hyperreal extension R ⊂ ⁎ R of the real numbers, the derivative of a real function y = f(x) at a real point x can be defined as the shadow of the quotient ∆y / ∆x for infinitesimal ∆x , where ∆y = f(x + ∆x) − f(x). Here the natural extension of f to the hyperreals is still denoted f . Here the derivative is said to exist if the shadow is independent of the infinitesimal chosen.
In higher dimensions
Vector-valued functions
A vector-valued function y of a real variable sends real numbers to vectors in some vector space R n . A vector-valued function can be split up into its coordinate functions y 1(t), y 2(t), ..., y n (t), meaning that y(t) = (y 1(t), ..., y n (t)). This includes, for example, parametric curves in R 2 or R 3. The coordinate functions are real valued functions, so the above definition of derivative applies to them. The derivative of y(t) is defined to be the vector, called the tangent vector, whose coordinates are the derivatives of the coordinate functions. That is,
Equivalently,
if the limit exists. The subtraction in the numerator is the subtraction of vectors, not scalars. If the derivative of y exists for every value of t, then y′ is another vector-valued function.
If e 1, ..., e n is the standard basis for R n , then y(t) can also be written as y 1(t)e 1 + ⋯ + y n (t)e n . If we assume that the derivative of a vector-valued function retains the linearity property, then the derivative of y(t) must be
because each of the basis vectors is a constant.
This generalization is useful, for example, if y(t) is the position vector of a particle at time t; then the derivative y′(t) is the velocity vector of the particle at time t.
Partial derivatives
Suppose that f is a function that depends on more than one variable—for instance,
f can be reinterpreted as a family of functions of one variable indexed by the other variables:
In other words, every value of x chooses a function, denoted fx , which is a function of one real number.[Note 3] That is,
Once a value of x is chosen, say a, then f(x, y) determines a function fa that sends y to a 2 + ay + y 2 :
In this expression, a is a constant, not a variable, so fa is a function of only one real variable. Consequently, the definition of the derivative for a function of one variable applies:
The above procedure can be performed for any choice of a. Assembling the derivatives together into a function gives a function that describes the variation of f in the y direction:
This is the partial derivative of f with respect to y. Here ∂ is a rounded d called the partial derivative symbol. To distinguish it from the letter d, ∂ is sometimes pronounced "der", "del", or "partial" instead of "dee".
In general, the partial derivative of a function f(x 1, …, x n ) in the direction xi at the point (a 1, ..., a n ) is defined to be:
In the above difference quotient, all the variables except xi are held fixed. That choice of fixed values determines a function of one variable
and, by definition,
In other words, the different choices of a index a family of one-variable functions just as in the example above. This expression also shows that the computation of partial derivatives reduces to the computation of one-variable derivatives.
This is fundamental for the study of the functions of several real variables. Let f(x 1, ..., x n ) be such a real-valued function. If all partial derivatives ∂f / ∂x j of f are defined at the point a = (a 1, ..., a n ), these partial derivatives define the vector
which is called the gradient of f at a . If f is differentiable at every point in some domain, then the gradient is a vector-valued function ∇f that maps the point (a 1, ..., a n ) to the vector ∇f(a 1, ..., a n ). Consequently, the gradient determines a vector field.
Directional derivatives
If f is a real-valued function on R n, then the partial derivatives of f measure its variation in the direction of the coordinate axes. For example, if f is a function of x and y, then its partial derivatives measure the variation in f in the x direction and the y direction. They do not, however, directly measure the variation of f in any other direction, such as along the diagonal line y = x . These are measured using directional derivatives. Choose a vector
The directional derivative of f in the direction of v at the point x is the limit
In some cases it may be easier to compute or estimate the directional derivative after changing the length of the vector. Often this is done to turn the problem into the computation of a directional derivative in the direction of a unit vector. To see how this works, suppose that v = λ u where u is a unit vector in the direction of v. Substitute h = k/λ into the difference quotient. The difference quotient becomes:
This is λ times the difference quotient for the directional derivative of f with respect to u. Furthermore, taking the limit as h tends to zero is the same as taking the limit as k tends to zero because h and k are multiples of each other. Therefore, D v (f) = λD u (f). Because of this rescaling property, directional derivatives are frequently considered only for unit vectors.
If all the partial derivatives of f exist and are continuous at x, then they determine the directional derivative of f in the direction v by the formula:
This is a consequence of the definition of the total derivative. It follows that the directional derivative is linear in v, meaning that D v + w (f) = D v (f) + D w (f).
The same definition also works when f is a function with values in R m . The above definition is applied to each component of the vectors. In this case, the directional derivative is a vector in R m .
Total derivative, total differential and Jacobian matrix
When f is a function from an open subset of R n to R m , then the directional derivative of f in a chosen direction is the best linear approximation to f at that point and in that direction. But when n > 1, no single directional derivative can give a complete picture of the behavior of f. The total derivative gives a complete picture by considering all directions at once. That is, for any vector v starting at a, the linear approximation formula holds:
Just like the single-variable derivative, f ′(a) is chosen so that the error in this approximation is as small as possible.
If n and m are both one, then the derivative f ′(a) is a number and the expression f ′(a)v is the product of two numbers. But in higher dimensions, it is impossible for f ′(a) to be a number. If it were a number, then f ′(a)v would be a vector in R n while the other terms would be vectors in R m , and therefore the formula would not make sense. For the linear approximation formula to make sense, f ′(a) must be a function that sends vectors in R n to vectors in R m , and f ′(a)v must denote this function evaluated at v.
To determine what kind of function it is, notice that the linear approximation formula can be rewritten as
Notice that if we choose another vector w, then this approximate equation determines another approximate equation by substituting w for v. It determines a third approximate equation by substituting both w for v and a + v for a. By subtracting these two new equations, we get
If we assume that v is small and that the derivative varies continuously in a, then f ′(a + v) is approximately equal to f ′(a), and therefore the right-hand side is approximately zero. The left-hand side can be rewritten in a different way using the linear approximation formula with v + w substituted for v. The linear approximation formula implies:
This suggests that f ′(a) is a linear transformation from the vector space R n to the vector space R m . In fact, it is possible to make this a precise derivation by measuring the error in the approximations. Assume that the error in these linear approximation formula is bounded by a constant times ||v||, where the constant is independent of v but depends continuously on a. Then, after adding an appropriate error term, all of the above approximate equalities can be rephrased as inequalities. In particular, f ′(a) is a linear transformation up to a small error term. In the limit as v and w tend to zero, it must therefore be a linear transformation. Since we define the total derivative by taking a limit as v goes to zero, f ′(a) must be a linear transformation.
In one variable, the fact that the derivative is the best linear approximation is expressed by the fact that it is the limit of difference quotients. However, the usual difference quotient does not make sense in higher dimensions because it is not usually possible to divide vectors. In particular, the numerator and denominator of the difference quotient are not even in the same vector space: The numerator lies in the codomain R m while the denominator lies in the domain R n . Furthermore, the derivative is a linear transformation, a different type of object from both the numerator and denominator. To make precise the idea that f ′(a) is the best linear approximation, it is necessary to adapt a different formula for the one-variable derivative in which these problems disappear. If f : R → R , then the usual definition of the derivative may be manipulated to show that the derivative of f at a is the unique number f ′(a) such that
This is equivalent to
because the limit of a function tends to zero if and only if the limit of the absolute value of the function tends to zero. This last formula can be adapted to the many-variable situation by replacing the absolute values with norms.
The definition of the total derivative of f at a, therefore, is that it is the unique linear transformation f ′(a) : R n → R m such that
Here h is a vector in R n , so the norm in the denominator is the standard length on R n . However, f′(a)h is a vector in R m , and the norm in the numerator is the standard length on R m . If v is a vector starting at a, then f ′(a)v is called the pushforward of v by f and is sometimes written f ∗ v .
If the total derivative exists at a, then all the partial derivatives and directional derivatives of f exist at a, and for all v, f ′(a)v is the directional derivative of f in the direction v. If we write f using coordinate functions, so that f = (f 1, f 2, ..., f m ), then the total derivative can be expressed using the partial derivatives as a matrix. This matrix is called the Jacobian matrix of f at a:
The existence of the total derivative f′(a) is strictly stronger than the existence of all the partial derivatives, but if the partial derivatives exist and are continuous, then the total derivative exists, is given by the Jacobian, and depends continuously on a.
The definition of the total derivative subsumes the definition of the derivative in one variable. That is, if f is a real-valued function of a real variable, then the total derivative exists if and only if the usual derivative exists. The Jacobian matrix reduces to a 1×1 matrix whose only entry is the derivative f′(x). This 1×1 matrix satisfies the property that f(a + h) − (f(a) + f ′(a)h) is approximately zero, in other words that
Up to changing variables, this is the statement that the function is the best linear approximation to f at a.
The total derivative of a function does not give another function in the same way as the one-variable case. This is because the total derivative of a multivariable function has to record much more information than the derivative of a single-variable function. Instead, the total derivative gives a function from the tangent bundle of the source to the tangent bundle of the target.
The natural analog of second, third, and higher-order total derivatives is not a linear transformation, is not a function on the tangent bundle, and is not built by repeatedly taking the total derivative. The analog of a higher-order derivative, called a jet, cannot be a linear transformation because higher-order derivatives reflect subtle geometric information, such as concavity, which cannot be described in terms of linear data such as vectors. It cannot be a function on the tangent bundle because the tangent bundle only has room for the base space and the directional derivatives. Because jets capture higher-order information, they take as arguments additional coordinates representing higher-order changes in direction. The space determined by these additional coordinates is called the jet bundle. The relation between the total derivative and the partial derivatives of a function is paralleled in the relation between the kth order jet of a function and its partial derivatives of order less than or equal to k.
By repeatedly taking the total derivative, one obtains higher versions of the Fréchet derivative, specialized to R p . The kth order total derivative may be interpreted as a map
which takes a point x in R n and assigns to it an element of the space of k-linear maps from R n to R m – the "best" (in a certain precise sense) k-linear approximation to f at that point. By precomposing it with the diagonal map Δ, x → (x, x), a generalized Taylor series may be begun as
where f(a) is identified with a constant function, x i − a i are the components of the vector x − a , and (Df) i and (D 2 f) jk are the components of Df and D 2 f as linear transformations.
Generalizations
The concept of a derivative can be extended to many other settings. The common thread is that the derivative of a function at a point serves as a linear approximation of the function at that point.
- An important generalization of the derivative concerns complex functions of complex variables, such as functions from (a domain in) the complex numbers C to C. The notion of the derivative of such a function is obtained by replacing real variables with complex variables in the definition. If C is identified with R 2 by writing a complex number z as x + iy , then a differentiable function from C to C is certainly differentiable as a function from R 2 to R 2 (in the sense that its partial derivatives all exist), but the converse is not true in general: the complex derivative only exists if the real derivative is complex linear and this imposes relations between the partial derivatives called the Cauchy–Riemann equations – see holomorphic functions.
- Another generalization concerns functions between differentiable or smooth manifolds. Intuitively speaking such a manifold M is a space that can be approximated near each point x by a vector space called its tangent space: the prototypical example is a smooth surface in R 3. The derivative (or differential) of a (differentiable) map f: M → N between manifolds, at a point x in M, is then a linear map from the tangent space of M at x to the tangent space of N at f(x). The derivative function becomes a map between the tangent bundles of M and N. This definition is fundamental in differential geometry and has many uses – see pushforward (differential) and pullback (differential geometry).
- Differentiation can also be defined for maps between infinite dimensional vector spaces such as Banach spaces and Fréchet spaces. There is a generalization both of the directional derivative, called the Gateaux derivative, and of the differential, called the Fréchet derivative.
- One deficiency of the classical derivative is that very many functions are not differentiable. Nevertheless, there is a way of extending the notion of the derivative so that all continuous functions and many other functions can be differentiated using a concept known as the weak derivative. The idea is to embed the continuous functions in a larger space called the space of distributions and only require that a function is differentiable "on average".
- The properties of the derivative have inspired the introduction and study of many similar objects in algebra and topology — see, for example, differential algebra.
- The discrete equivalent of differentiation is finite differences. The study of differential calculus is unified with the calculus of finite differences in time scale calculus.
- Also see arithmetic derivative.
History
Calculus, known in its early history as infinitesimal calculus, is a mathematical discipline focused on limits, functions, derivatives, integrals, and infinite series. Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz independently discovered calculus in the mid-17th century. However, each inventor claimed the other stole his work in a bitter dispute that continued until the end of their lives.
See also
- Applications of derivatives
- Automatic differentiation
- Differentiability class
- Differentiation rules
- Differintegral
- Fractal derivative
- Generalizations of the derivative
- Hasse derivative
- History of calculus
- Integral
- Infinitesimal
- Linearization
- Mathematical analysis
- Multiplicative inverse
- Numerical differentiation
- Rate (mathematics)
- Radon–Nikodym theorem
- Symmetric derivative
- Schwarzian derivative
Notes
- ^ Differential calculus, as discussed in this article, is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See Apostol 1967, Apostol 1969, and Spivak 1994.
- ^ In the formulation of calculus in terms of limits, the du symbol has been assigned various meanings by various authors. Some authors do not assign a meaning to du by itself, but only as part of the symbol du/dx. Others define dx as an independent variable, and define du by du = dx⋅f ′(x). In non-standard analysis du is defined as an infinitesimal. It is also interpreted as the exterior derivative of a function u. See differential (infinitesimal) for further information.
- ^ This can also be expressed as the operation known as currying.
References
- ^ Banach, S. (1931), "Uber die Baire'sche Kategorie gewisser Funktionenmengen", Studia Math., 3 (3): 174–179, doi:10.4064/sm-3-1-174-179. . Cited by Hewitt, E; Stromberg, K (1963), Real and abstract analysis, Springer-Verlag, Theorem 17.8
- ^ Apostol 1967, §4.18
- ^ Manuscript of November 11, 1675 (Cajori vol. 2, page 204)
- ^ "The Notation of Differentiation". MIT. 1998. Retrieved 24 October 2012.
- ^ Evans, Lawrence (1999). Partial Differential Equations. American Mathematical Society. p. 63. ISBN0-8218-0772-2.
- ^ Kreyszig, Erwin (1991). Differential Geometry. New York: Dover. p. 1. ISBN0-486-66721-9.
Bibliography
- Anton, Howard; Bivens, Irl; Davis, Stephen (February 2, 2005), Calculus: Early Transcendentals Single and Multivariable (8th ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN978-0-471-47244-5
- Apostol, Tom M. (June 1967), Calculus, Vol. 1: One-Variable Calculus with an Introduction to Linear Algebra , vol. 1 (2nd ed.), Wiley, ISBN978-0-471-00005-1
- Apostol, Tom M. (June 1969), Calculus, Vol. 2: Multi-Variable Calculus and Linear Algebra with Applications , vol. 1 (2nd ed.), Wiley, ISBN978-0-471-00007-5
- Courant, Richard; John, Fritz (December 22, 1998), Introduction to Calculus and Analysis, Vol. 1, Springer-Verlag, ISBN978-3-540-65058-4
- Eves, Howard (January 2, 1990), An Introduction to the History of Mathematics (6th ed.), Brooks Cole, ISBN978-0-03-029558-4
- Larson, Ron; Hostetler, Robert P.; Edwards, Bruce H. (February 28, 2006), Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions (4th ed.), Houghton Mifflin Company, ISBN978-0-618-60624-5
- Spivak, Michael (September 1994), Calculus (3rd ed.), Publish or Perish, ISBN978-0-914098-89-8
- Stewart, James (December 24, 2002), Calculus (5th ed.), Brooks Cole, ISBN978-0-534-39339-7
- Thompson, Silvanus P. (September 8, 1998), Calculus Made Easy (Revised, Updated, Expanded ed.), New York: St. Martin's Press, ISBN978-0-312-18548-0
Online books
- Crowell, Benjamin (2017), Fundamentals of Calculus
- (Govt. of TN), TamilNadu Textbook Corporation (2006), Mathematics- vol.2 (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-01-15, retrieved 2014-11-29
- Garrett, Paul (2004), Notes on First-Year Calculus, University of Minnesota
- Hussain, Faraz (2006), Understanding Calculus
- Keisler, H. Jerome (2000), Elementary Calculus: An Approach Using Infinitesimals
- Mauch, Sean (2004), Unabridged Version of Sean's Applied Math Book, archived from the original on 2006-04-15
- Sloughter, Dan (2000), Difference Equations to Differential Equations
- Strang, Gilbert (1991), Calculus
- Stroyan, Keith D. (1997), A Brief Introduction to Infinitesimal Calculus
- Wikibooks, Calculus
External links
- "Derivative", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Khan Academy: "Newton, Leibniz, and Usain Bolt"
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Derivative". MathWorld.
- Online Derivative Calculator from Wolfram Alpha.
bedardcatelleaden.blogspot.com
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derivative
























































































Postar um comentário for "How to Determine if Something is Continues in a Dervative"